lv pv vg|difference between raid and lvm : 2024-10-22 Add the PV to the Volume Group (VG) and then extend the Logical Volume (LV). Look at the picture below. The red line mark shows the original size of the root mount point. Get ready, because a return to aviator shades is happening this year. The runways were flooded with this ageless-classic style. Shop these Reznor retro sunnies for the latest 90's rimless mid square design. Size: 138 mm 67 mm 55 mm 7 mm 145 mm Specs: AviatorSquareRetro PC Resin NO UV400 Protection.
0 · vgdisplay
1 · pv vg lv linux
2 · lvm vgcreate
3 · lvm explained
4 · linux what is lvm
5 · difference between raid and lvm
6 · difference between l and lvm
7 · add existing partition to lvm
54 Malta Ave, Brampton, ON L6Y 5E9. (289) 801-4368. 6 Photos. 1-3 Bedrooms. 662-1,160 Square Feet. Property Information. 198 Units. 12 Stories. Bayanihan Non Profit Cooperative Homes Description. Bayanihan Non Profit Cooperative Homes in Brampton, ON is ready for your visit.
lv pv vg*******LVM, or Logical Volume Management, is a storage device management technology that gives users the power to pool and abstract .lv pv vgYou can create an LVM volume group (VG) myvg using the /dev/vdb1 and /dev/vdb2 physical volumes (PVs). By default, when physical volumes are used to create a volume .
lv pv vg difference between raid and lvm Most modern Linux distributions are LVM-aware to have their root file systems on a logical volume. Logical Volume Management (LVM) manages three main components: Physical Volume (PV) is the . A Logical Volume (LV) is a virtual block device that can be used by the system or applications. Each block of data in an LV is stored on one or more PV in the VG, according to algorithms implemented by .
Add the PV to the Volume Group (VG) and then extend the Logical Volume (LV). Look at the picture below. The red line mark shows the original size of the root mount point. Add the PV to the Volume Group (VG) and then extend the Logical Volume (LV). Look at the picture below. The red line mark shows the original size of the root mount point.A logical volume is a virtual, block storage device that a file system, database, or application can use. To create an LVM logical volume, the physical volumes (PVs) are combined .

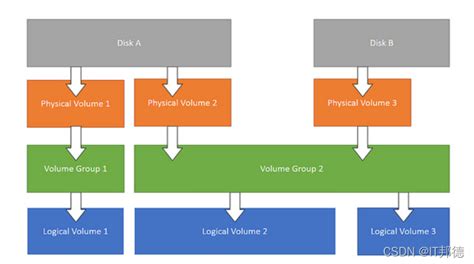
Physical volumes (PV) are the base "block" that you need in order to manipulate a disk using Logical Volume Manager (LVM). Now, let’s not rush ahead. What exactly is a physical volume?
In this tutorial, you'll learn the concept of LVM, its components and why you should be using it. I won't be limited to just the theoretical explanation. I'll also show hands-on examples for creating .difference between raid and lvm Step 1: List backup file to restore LVM metadata in Linux. Step 2: Restore PV (Physical Volume) in Linux. Step 3: Restore VG to recover LVM2 partition. Step 4: Activate the Volume Group. Step 5: . LVM, or Logical Volume Management, is a storage device management technology that gives users the power to pool and abstract the physical layout of component storage devices for flexible administration. This is accomplished by designating the storage disks as Physical Volumes (PV), or storage capacity useable by LVM. The PVs are then added to one or more Volume Groups (VGs). The VGs are carved into one or more Logical Volumes (LVs), which then are treated as traditional partitions.
You can create an LVM volume group (VG) myvg using the /dev/vdb1 and /dev/vdb2 physical volumes (PVs). By default, when physical volumes are used to create a volume group, its disk space is divided into 4MB extents.
Most modern Linux distributions are LVM-aware to have their root file systems on a logical volume. Logical Volume Management (LVM) manages three main components: Physical Volume (PV) is the partition of the physical disks. Volume Group (VG) is a combination of multiple individual hard drives/or disk partitions into a single volume . A Logical Volume (LV) is a virtual block device that can be used by the system or applications. Each block of data in an LV is stored on one or more PV in the VG, according to algorithms implemented by Device Mapper (DM) in the kernel.
Add the PV to the Volume Group (VG) and then extend the Logical Volume (LV). Look at the picture below. The red line mark shows the original size of the root mount point.A logical volume is a virtual, block storage device that a file system, database, or application can use. To create an LVM logical volume, the physical volumes (PVs) are combined into a volume group (VG). This creates a pool of disk space out of which LVM logical volumes (LVs) can be allocated. 5.1. Overview of logical volumes. Copy link.
Physical volumes (PV) are the base "block" that you need in order to manipulate a disk using Logical Volume Manager (LVM). Now, let’s not rush ahead. What exactly is a physical volume? In this tutorial, you'll learn the concept of LVM, its components and why you should be using it. I won't be limited to just the theoretical explanation. I'll also show hands-on examples for creating and managing LVMs in Linux. Step 1: List backup file to restore LVM metadata in Linux. Step 2: Restore PV (Physical Volume) in Linux. Step 3: Restore VG to recover LVM2 partition. Step 4: Activate the Volume Group. Step 5: Verify the data loss after LVM2 partition recovery. Prepare Lab Environment. LVM, or Logical Volume Management, is a storage device management technology that gives users the power to pool and abstract the physical layout of component storage devices for flexible administration. This is accomplished by designating the storage disks as Physical Volumes (PV), or storage capacity useable by LVM. The PVs are then added to one or more Volume Groups (VGs). The VGs are carved into one or more Logical Volumes (LVs), which then are treated as traditional partitions.You can create an LVM volume group (VG) myvg using the /dev/vdb1 and /dev/vdb2 physical volumes (PVs). By default, when physical volumes are used to create a volume group, its disk space is divided into 4MB extents. Most modern Linux distributions are LVM-aware to have their root file systems on a logical volume. Logical Volume Management (LVM) manages three main components: Physical Volume (PV) is the partition of the physical disks. Volume Group (VG) is a combination of multiple individual hard drives/or disk partitions into a single volume .
A Logical Volume (LV) is a virtual block device that can be used by the system or applications. Each block of data in an LV is stored on one or more PV in the VG, according to algorithms implemented by Device Mapper (DM) in the kernel. Add the PV to the Volume Group (VG) and then extend the Logical Volume (LV). Look at the picture below. The red line mark shows the original size of the root mount point.A logical volume is a virtual, block storage device that a file system, database, or application can use. To create an LVM logical volume, the physical volumes (PVs) are combined into a volume group (VG). This creates a pool of disk space out of which LVM logical volumes (LVs) can be allocated. 5.1. Overview of logical volumes. Copy link. Physical volumes (PV) are the base "block" that you need in order to manipulate a disk using Logical Volume Manager (LVM). Now, let’s not rush ahead. What exactly is a physical volume?
Rolex 69174 Overview. The Rolex Datejust 69174 has a last known retail price of $2,800 and trades for $4,006 on the pre-owned market. Expect .
lv pv vg|difference between raid and lvm